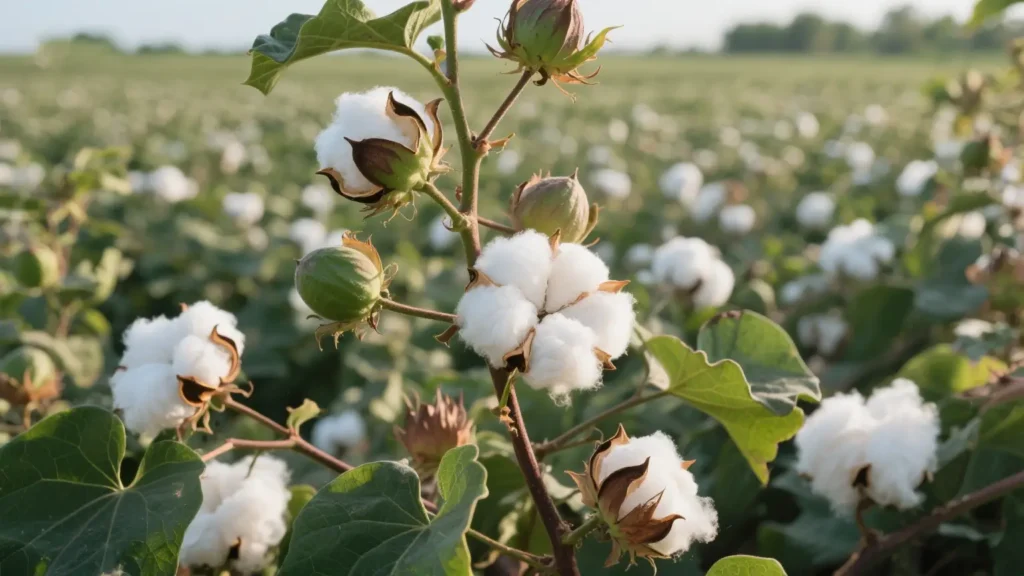
Crop: Cotton
Overview
Cotton Crop Management Recommendations
⛳ Use Resistant Varieties: For seed treatment to protect seedlings, use Imidacloprid 600g/l FS. Selecting varieties adapted to local climate and soil conditions is fundamental.
⛳ Field Sanitation: Before sowing, control early weeds with Glyphosate 360 g/L SL. Maintaining clean fields by removing previous crop residues further reduces pest habitats.
⛳ Crop Rotation: To control soil-borne nematodes after legumes, apply Cadusafos 100 g/L EC. Rotating with non-host crops breaks pest cycles, improves soil structure.
⛳ Regular Scouting: Upon detecting bollworms, spray Emamectin Benzoate 5% SG. Consistent monitoring helps in early detection of nutrient deficiencies.
⛳ Timely Chemical Control: For aphid and whitefly outbreaks, use Acetamiprid 20% SP. Implementing integrated pest management, including biological controls.
⛳ Balanced Fertilization & Irrigation: To prevent fungal wilts, apply Carbendazim 50% WP to the root zone.
Common Cotton Diseases
1. Bacterial Blight
- Impact: Reduces leaf area and boll formation.
-
Symptoms: Angular, water-soaked spots on leaves, stems, and bolls that turn dark brown.
-
Management: Spray Kasugamycin 2% SL at disease onset or after rain/wind.
2. Fusarium Wilt
- Impact: Causes plant wilting and death.
-
Symptoms: Wilting from lower leaves upward, brown vascular discoloration, plant death.
-
Management: Apply Carboxin·Thiram 40% SC as soil drench during transplanting.
3. Verticillium Wilt
- Impact: Reduces boll development and yield.
-
Symptoms: Yellow patches on lower leaves, leaf scorch, vascular browning, slow defoliation.
-
Management: Treat seeds with Fludioxonil 25 g/L FS before sowing.
4. Boll Rot
-
Impact: Directly reduces yield and severely compromises fiber quality, leading to significant economic loss.
-
Symptoms: Brown or pink mold on bolls, causing rot, stiffened locks, or shedding.
-
Management: Spray Azoxystrobin 250 g/L SC during boll formation in wet weather.
Common Cotton Pests
1. Cotton Bollworm
-
Identification: Larvae bore into and feed on cotton buds, flowers, and bolls, causing abscission or boll rot. It is a primary pest causing significant yield loss.,
-
Management: Apply Chlorantraniliprole 200 g/L SC as a foliar spray during peak egg hatching, before larvae bore into the bolls.
2. Cotton Aphid
-
Identification: Colonies cluster on the undersides of young leaves and stems to suck sap, leading to leaf curling and a shiny appearance. They excrete honeydew, which promotes sooty mold.,
-
Management: At the first sign of infestation, spray with Thiamethoxam 25% WG, which has systemic action.
3. Whiteflies
-
Identification: Adults and nymphs feed on the undersides of leaves, causing chlorosis and wilting. They also excrete honeydew and can transmit viral diseases.,
-
Management: At the early stages of infestation, apply Bifenthrin 100 g/L EC or Spirotetramat 22.4% SC for control.
4. Red Spider Mite
-
Identification: Tiny mites that feed on the undersides of leaves, causing stippling (yellow-white spots). Severe infestations lead to reddish-brown, desiccated leaves that drop prematurely.,
-
Management: At the initial, localized stages, use Abamectin 1.8% EC or Pyridaben 15% EC for targeted spraying, ensuring thorough coverage of the leaf undersides.
Common Weeds in Cotton Fields
1. Large Crabgrass
-
Identification: An annual grass weed with stems that spread along the ground and root at the nodes. Highly competitive for nutrients and water.
-
Management: Apply Quizalofop-P-ethyl 50 g/L EC as a post-emergence spray before canopy closure.
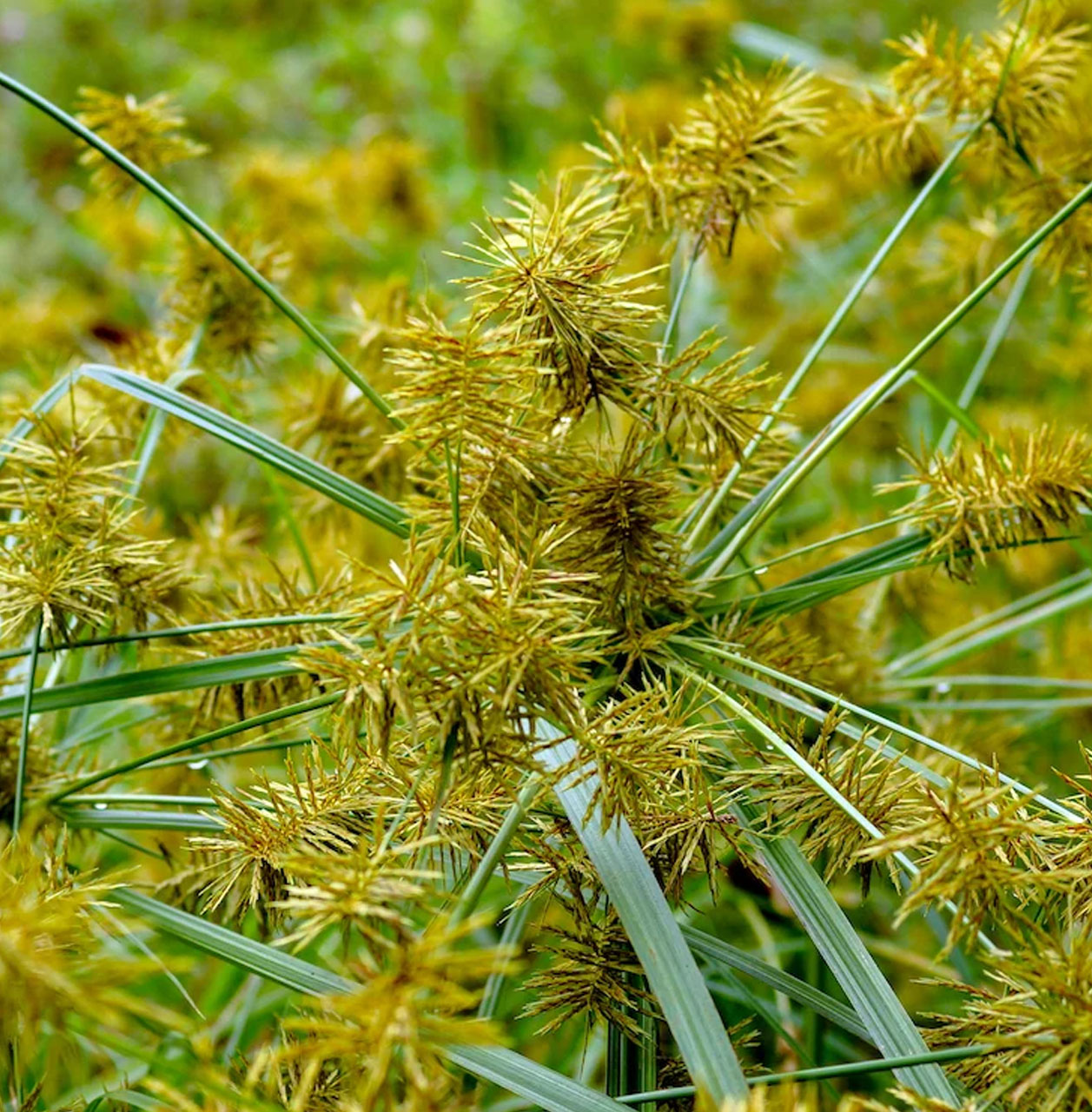
2. Nutsedge
-
Identification: A perennial sedge with triangular stems and underground tubers. Extremely difficult to eradicate due to strong regrowth.
-
Management: Use Trifloxysulfuron 75% WG for directed spraying during mid-to-late growth stages.
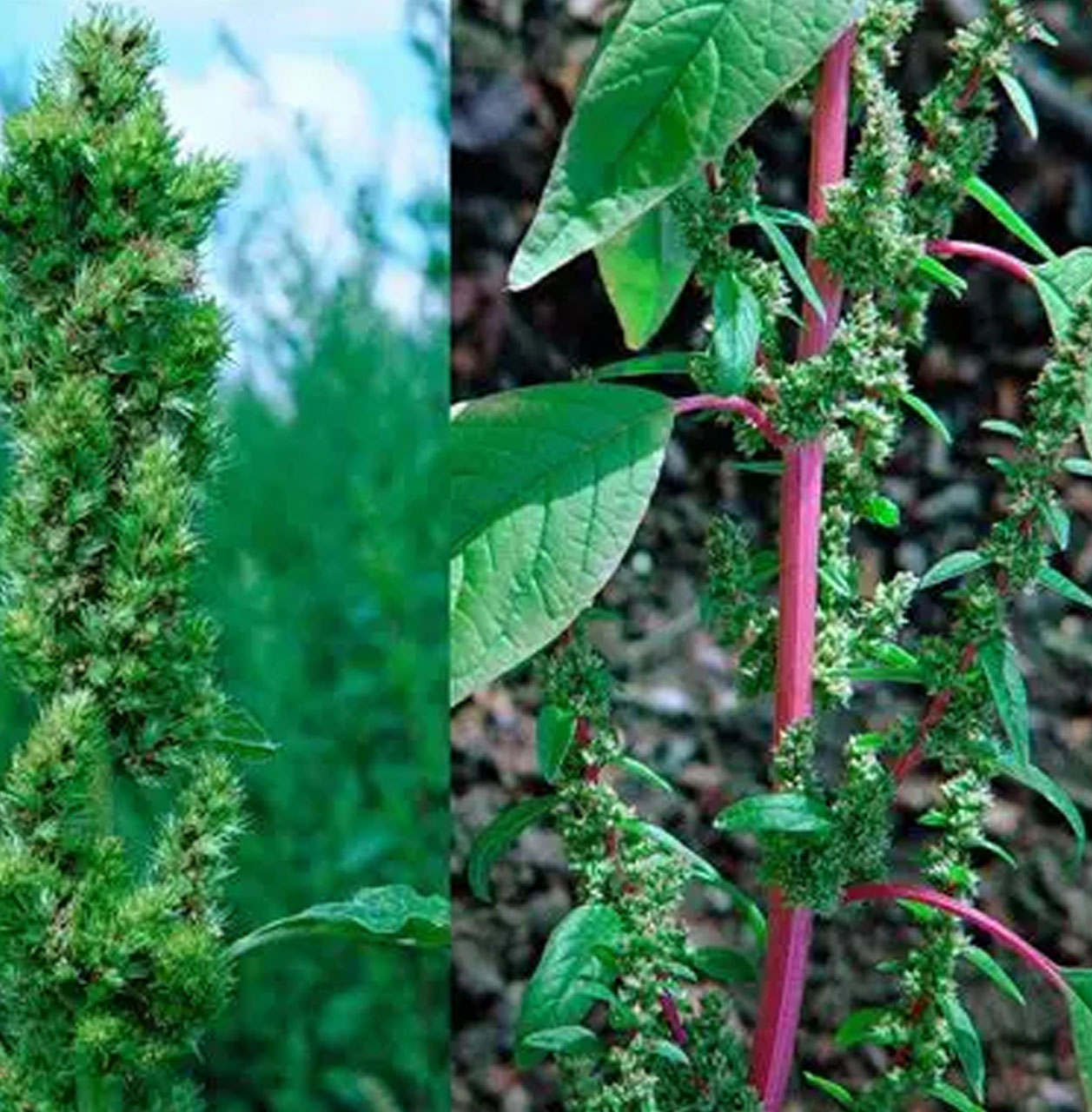
3. Pigweed
-
Identification: An annual broadleaf weed with broad leaves and reddish stems. Adaptable and fast-growing, depleting soil nutrients.
-
Management: Spray Fluoroglycofen 10% EC at the seedling stage for rapid contact control.
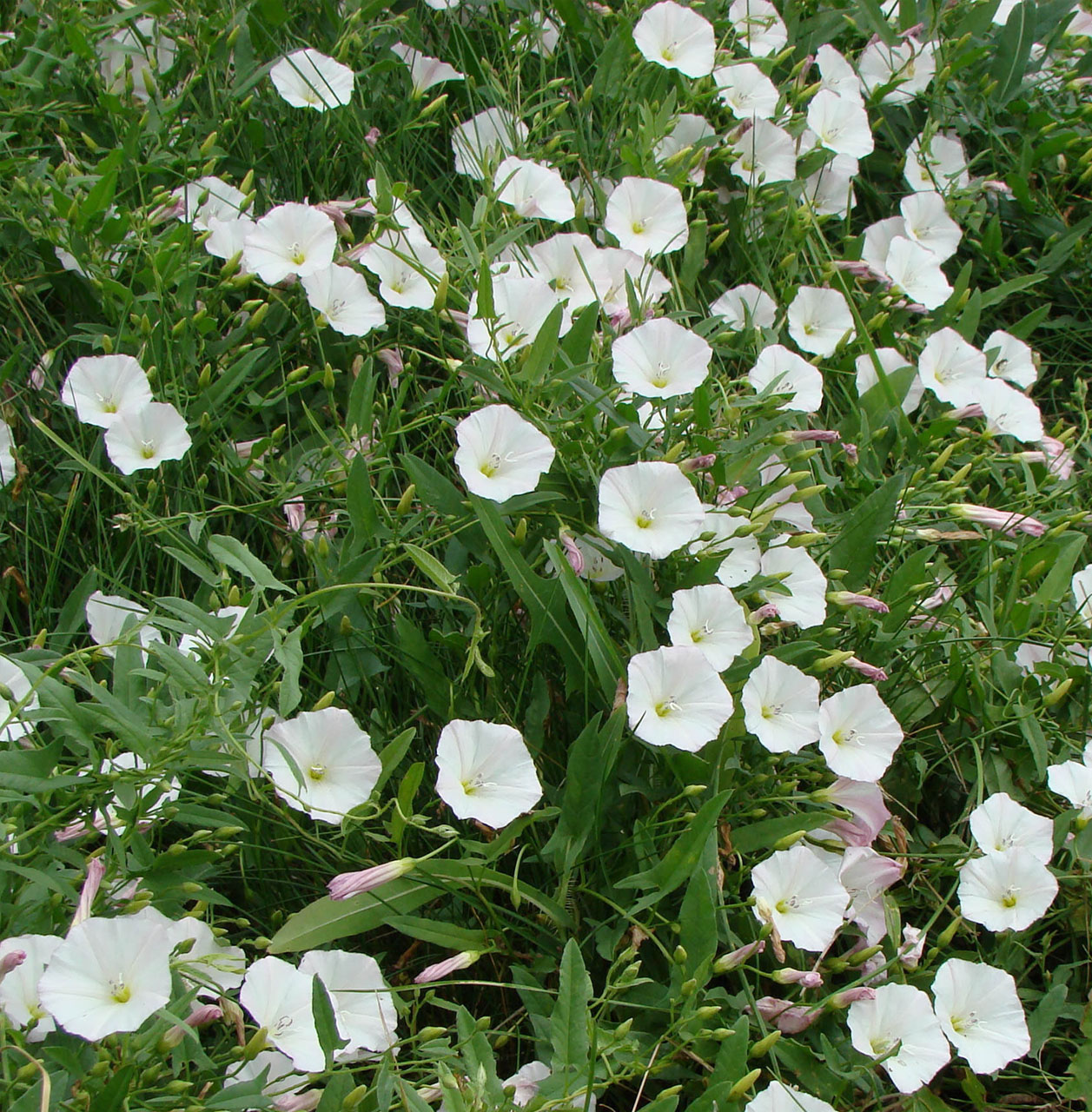
4. Field Bindweed
-
Identification: A perennial broadleaf vine that twines around cotton plants, competing for light and hindering harvesting.
-
Management: Apply Glufosinate ammonium 200 g/L SL as a directed spray during vigorous growth, avoiding contact with cotton leaves.